how to interpret tukey hsd results|13.6: Post‐hoc Analysis – Tukey’s Honestly Significant Difference : Tuguegarao The model will be the Tukey \(\mathrm{HSD}\) test. Here are the differences of the sample means for each pair ranked from lowest to highest: Test 1: Cupertino to San Jose : . Eggs are also rich in lutein, a compound that hydrates your hair and improves the hair softness; Lutein in egg yolk will help with brittle hair, prevent breakage and split-ends, and improve the texture of your .
how to interpret tukey hsd results,Yes you can interpret this like any other p-value, meaning that none of your comparisons are statistically significant. You can also check ?TukeyHSD and then under Value it says: A list of class c("multicomp", "TukeyHSD"), with one component for each term requested in which.Learn how to report the results of a one-way ANOVA with Tukey HSD test for multiple comparisons. See an example of how to write the general structure and i.
The model will be the Tukey \(\mathrm{HSD}\) test. Here are the differences of the sample means for each pair ranked from lowest to highest: Test 1: Cupertino to San Jose : .
how to interpret tukey hsd resultsTukey's HSD (“honestly significant difference”) is the most common post hoc test for ANOVA. It is listed under “equal variances assumed”, which refers to the homogeneity assumption. However, this is not needed for our data because .
how to interpret tukey hsd results 13.6: Post‐hoc Analysis – Tukey’s Honestly Significant Difference Tukey's HSD (“honestly significant difference”) is the most common post hoc test for ANOVA. It is listed under “equal variances assumed”, which refers to the homogeneity assumption. However, this is not needed for our data because . Learn how to use post hoc tests to compare multiple group means after a statistically significant ANOVA result. Compare Tukey HSD, Bonferroni, and Games-Howell tests and their benefits and drawbacks.
Learn how to use Tukey HSD (Honestly Significant Difference) test to compare multiple group means and control the experiment-wise error rate. See examples, formulas, worksheet functions, and critical values for the Studentized Range q .
In this tutorial, we’ll look at how to perform a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) for independent groups in SPSS, and how to interpret the result using Tukey’s HSD. Quick Steps. Click on Analyze -> Compare Means -> One-Way .
The Tukey Test (or Tukey procedure), also called Tukey’s Honest Significant Difference test, is a post-hoc test based on the studentized range distribution. An ANOVA test can tell you if your .The test statistic. Tukey's test is based on a formula very similar to that of the t -test. In fact, Tukey's test is essentially a t -test, except that it corrects for family-wise error rate . The . If you put all these pair-wise tests together, you can generate an overall interpretation of Tukey’s HSD results that discusses sets of groups that are not detectably .When reporting the result it’s normal to reference both the ANOVA test and the post hoc Tukey HSD test. Thus, given our example here, you could write something like: There was a statistically significant difference between groups .
How to interpret grouping result in Tukey's HSD test. Ask Question Asked 7 years ago. Modified 5 years ago. Viewed 3k times 2 $\begingroup$ Assuming there are three methods to kill bugs, and we want to know whether their performance differs. The Tukey's HSD test gives the following grouping results: The Tukey HSD test is a way of reporting ANOVA results and determining if the relationship between three independently varying quantities is statistically significant. It relies on first collecting values from a standard ANOVA test and then using specialized programs or sites for the Tukey HSD. 2. Interpreting the Tukey's HSD Results. The results of the Tukey's HSD analysis are presented in a table that shows the pairwise comparisons of the means. Each row in the table represents a comparison between two means, and the columns show the mean difference, the standard error, the lower and upper confidence interval, and the p-value.After you have run an ANOVA and found significant results, then you can run Tukey’s HSD to find out which specific groups’s means (compared with each other) are different. The test compares all possible pairs of means. General Steps. Step 1: Perform the ANOVA test. Assuming your F value is significant, you can run the post hoc test.

Tukey HSD Test in R, When there are three or more independent groups, we apply a one-way ANOVA to see if there is a significant difference. The p-value for one-way ANOVA is less than 0.05 indicate that at least one of the treatment groups differs from the others.

After you have run an ANOVA and found significant results, then you can run Tukey’s HSD to find out which specific group means, when compared with each other, are different. The test compares all possible pairs of group means. . If that confidence interval contains the value of zero, you will interpret that to mean the two group means you .
Since this is less than .05, we have sufficient evidence to say that the mean values across each group are not equal. Thus, we can proceed to perform Tukey’s Test to determine exactly which group means are different. Step 2: Perform Tukey’s Test. The following code shows how to use the TukeyHSD() function to perform Tukey’s Test:
28 When this procedure is used with unequal group sizes it is also sometimes called Tukey-Kramer's method.. 29 We often use "spurious" to describe falsely rejected null hypotheses which are also called false detections.. 30 The plot of results usually contains all the labels of groups but if the labels are long or there many groups, sometimes the row labels are hard to see even . Yes, your interpretation is generally correct. TukeyHSD() is simply a Student's t-test, like you ran before, adjusted for multiple comparisons. Tukey's procedure assumes the following: Independence of observations; Homoscedasticity; The Fisher's LSD test is a similar and useful analysis, though it does not correct for multiple comparisons like . How to run and interpret a Tukey HSD (Honestly Significant Difference) post hoc test in SPSS. I am looking for a way to save the results to save the results of the Tukeyhsd into a pandas dataframe. see below: import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import statsmodels.formula.api as smf import . (Results) Multiple Comparison of Means - Tukey HSD,FWER=0.05 ===== group1 group2 meandiff lower upper reject ----- A B 20.35 7.388 33.312 True A C -3. .13.6: Post‐hoc Analysis – Tukey’s Honestly Significant Difference Tukey test is a single-step multiple comparison procedure and statistical test. It is a post-hoc analysis, what means that it is used in conjunction with an ANOVA. It allows to find means of a factor that are significantly different from each other, comparing all possible pairs of means with a t-test like method.Perform Tukey’s HSD test for equality of means over multiple treatments. Tukey’s honestly significant difference (HSD) test performs pairwise comparison of means for a set of samples. Whereas ANOVA (e.g. f_oneway) assesses whether the true means underlying each sample are identical, Tukey’s HSD is a post hoc test used to compare the mean .I would love to perform a TukeyHSD post-hoc test after my two-way Anova with R, obtaining a table containing the sorted pairs grouped by significant difference. (Sorry about the wording, I'm still . I'm having trouble exporting my TukeyHSD results so that they are separated in cells when I open the results up in something like Excel. I tried using write.csv() but it says: . selected output for Tukey's HSD in two-way ANOVA in . I normally would expect the p-value from the aov summary to be expressed as Pr(>F), so I'm a little fuzzy on the results I've obtained. Also, can someone help me understand the Tukey multiple comparisons of means results? I'm not totally clear on what the diff and p adj results indicate. The results shown here are an abridged version of what I .Use TukeyHSD() to conduct to evaluate all pairwise comparisons. Store the result in tukey. Call plot() on the result from Tukey's procedure to plot confidence intervals for the mean differences of the different pairwise comparisons.
how to interpret tukey hsd results|13.6: Post‐hoc Analysis – Tukey’s Honestly Significant Difference
PH0 · tukey hsd test
PH1 · Using Post Hoc Tests with ANOVA
PH2 · Tukey's range test
PH3 · Tukey Test / Tukey Procedure / Honest Significant Difference
PH4 · Tukey HSD (Honestly Sig Diff)
PH5 · The Complete Guide: How to Report ANOVA Results
PH6 · SPSS ANOVA with Post Hoc Tests
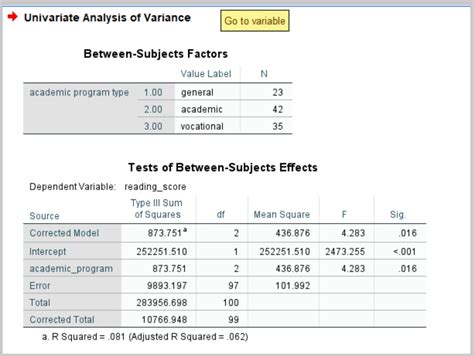
PH7 · One Way ANOVA in SPSS Including Interpretation
PH8 · 3.6: Multiple (pair
PH9 · 13.6: Post‐hoc Analysis – Tukey’s Honestly Significant Difference